Rare cancer types are classified based on the number of people affected each year. Usually, cancers that are categorized under rare types affect less than one in a hundred thousand people every year. However, such rare types of cancers have different types. But people affected with each type of rare cancer are fewer in number. People may hear about some of the rare cancers like thyroid cancer, mouth cancer, and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), but many more are there which you may not hear.
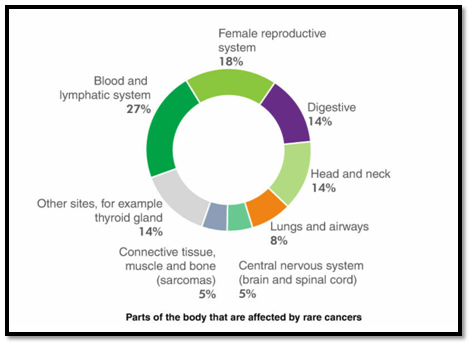
The following diagram helps to understand which body parts get affected by rare cancers. Approx. 1 in 5 people affected with rare cancers in the blood and lymphatic system including some specific types of lymphoma and leukemia.
Following are A to Z alphabetically ordered rare cancer types:
- 5q- syndrome: This is a type of rare blood cancer that occurs due to a genetic disorder.
- Acinic cell carcinoma: This is a salivary gland type cancer of the breast.
- Acral lentiginous melanoma: This is a type of melanoma skin cancer that develops in the palm or sole.
- Acromegaly: Endocrinal disorder leads to bone changes, abnormal growth, and hand and feet inflammation.
- Acrospiroma: Detail information not found.
- ACTH-secreting pituitary adenoma: Tumor in the pituitary gland.
- Acute erythroid leukemia: This is a type of blood cancer.
- Acute leukemia of ambiguous lineage: This is a type of blood cancer.
- Acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Bone marrow generates uncontrolled lymphocytes.
- Acute lymphoblastic leukemia congenital sporadic aniridia: Genetic abnormality leads to rare cancer development.
- Acute megakaryoblastic leukemia: Rare childhood cancer occurs mainly in Down syndrome patients.
- Acute monoblastic leukemia: Rare blood cancer.
- Acute myeloblastic leukemia with maturation: Rare blood cancer with the characteristic feature of granulocytic maturation.
- Acute myeloblastic leukemia without maturation: Rare blood cancer with the characteristic features of no myeloid maturation.
- Acute myelomonocytic leukemia
- Acute non lymphoblastic leukemia
- Acute panmyelosis with myelofibrosis
- Acute promyelocytic leukemia
- Adenocarcinoid tumor
- Adenocarcinoma of the appendix
- Adenoid cystic carcinoma
- Adenosarcoma of the uterus
- Adrenal cancer
- Adrenal medulla cancer
- Adrenocortical carcinoma
- Aggressive NK cell leukemia
- Aicardi syndrome
- Alveolar soft part sarcoma
- Ameloblastic carcinoma
- AML with myelodysplasia-related features
- Anal cancer
- Anaplastic astrocytoma
- Anaplastic ependymoma
- Anaplastic ganglioglioma
- Anaplastic large cell lymphoma
- Anaplastic oligoastrocytoma
- Anaplastic oligodendroglioma
- Anaplastic plasmacytoma
- Anaplastic small cell lymphoma
- Anaplastic thyroid cancer
- Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma
- Angioma hereditary neurocutaneous
- Angioma serpiginosum
- Angiosarcoma of the breast
- Angiosarcoma of the liver
- Angiosarcoma of the scalp
- Astroblastoma
- Ataxia telangiectasia
- Atrial myxoma, familial
- Autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome
- B cell prolymphocytic leukemia
- B-cell lymphoma
- Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba syndrome
- Basal cell carcinoma, infundibulocystic
- Basal cell carcinoma, multiple
- Bazex-Dupre-Christol syndrome
- Becker nevus syndrome
- Bednar tumor
- Benign metastasizing leiomyoma
- Benign multicystic peritoneal mesothelioma
- Bile duct cancer
- Biliary tract cancer
- Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome
- Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell
- Bloom syndrome
- Blue rubber bleb nevus syndrome
- Bowen’s disease
- Brain stem cancer
- Brain tumor, adult
- Brain tumor, childhood
- BRCA1 hereditary breast and ovarian cancer syndrome
- BRCA2 hereditary breast and ovarian cancer syndrome
- Breast cancer, male
- Brenner tumor of ovary
- Brenner tumor of the vagina
- Bronchial adenomas/carcinoids childhood
- Burkitt lymphoma
- Buschke-Lowenstein tumor
- Carcinoid syndrome
- Carcinoid tumor
- Carcinoid tumor childhood
- Carcinoma of the vocal tract
- Carney complex
- Carney triad
- Carotid body tumor
- Cartilaginous cancer
- CDK4 linked melanoma
- Central nervous system germinoma
- Central neurocytoma
- Cerebellar astrocytoma, childhood
- Cerebellar liponeurocytoma
- Cerebral astrocytoma, childhood
- Cerebral sarcoma
- Cerebral ventricle cancer
- Cerebro-oculo-facio-skeletal syndrome
- Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia
- CHILD syndrome
- Childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- Childhood brain stem glioma
- Childhood hepatocellular carcinoma
- Childhood Supratentorial Embryonal Tumor, Not Otherwise Specified
- Chondrosarcoma
- Chordoid glioma of the third ventricle
- Chordoma
- Choriocarcinoma
- Choroid plexus carcinoma
- Choroid plexus papilloma
- Chromophil renal cell carcinoma
- Chromophobe renal cell carcinoma
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
- Chronic myeloid leukemia
- Chronic myelomonocytic leukemia
- Chronic myeloproliferative disorders
- Chronic neutrophilic leukemia
- Clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- CLOVES syndrome
- Cockayne syndrome type I
- Cockayne syndrome type II
- Cockayne syndrome type III
- Collecting duct carcinoma
- Common variable immunodeficiency
- Costello syndrome
- Cowden syndrome
- Craniopharyngioma
- Cronkhite-Canada disease
- Cutaneous mastocytoma
- Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
- Deafness-lymphedema-leukemia syndrome
- Dendritic cell tumor
- Denys-Drash syndrome
- Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans
- Desmoid tumor
- Desmoplastic infantile astrocytoma
- Desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma
- Desmoplastic small round cell tumor
- Diamond-Blackfan anemia
- Diaphyseal medullary stenosis with malignant fibrous histiocytoma
- Diffuse astrocytoma
- Diffuse cavernous hemangioma of the rectum
- Diffuse gastric cancer
- Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
- Digestive System Melanoma
- Disseminated peritoneal leiomyomatosis
- Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor
- Dyskeratosis congenita
- Dyskeratosis congenita autosomal dominant
- Dyskeratosis congenita autosomal recessive
- Dyskeratosis congenita X-linked
- Eccrine mucinous carcinoma
- Eccrine porocarcinoma
- Embryonal carcinoma
- Embryonal sarcoma
- Embryonal tumor with multilayered rosettes
- Enchondroma
- Endemic Kaposi sarcoma
- Endometrial stromal sarcoma
- Enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma
- Ependymoma
- Epithelial-myoepithelial carcinoma
- Esophageal cancer
- Essential thrombocythemia
- Ewing sarcoma
- Extragonadal germ cell tumor
- Extramammary Paget disease
- Fallopian tube cancer
- Familial adenomatous polyposis
- Familial colorectal cancer
- Familial hyperaldosteronism type 2
- Familial pancreatic cancer
- Familial platelet disorder with associated myeloid malignancy
- Familial prostate cancer
- Familial Wilms tumor 2
- Fanconi anemia
- Fibrolamellar carcinoma
- Fibrosarcoma
- Follicular lymphoma
- Frasier syndrome
- Functioning pancreatic endocrine tumor
- Gallbladder cancer
- Gangliocytoma
- Ganglioglioma
- Gardner syndrome
- Gastric lymphoma
- Gastric Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
- Gastro-enteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumor
- Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors
- Giant cell tumor of bone
- Giant congenital nevus
- Glassy cell carcinoma of the cervix
- Glioblastoma
- Glioma
- Gliosarcoma
- Glomus jugulare tumors
- Glomus tympanicum tumor
- Glomus vagale tumor
- Glucagonoma
- Goblet cell carcinoid
- Granular cell tumor
- Granulomatous slack skin disease
- Granulosa cell tumor of the ovary
- Gray zone lymphoma
- Gynandroblastoma
- Hairy cell leukemia
- Heart tumor
- Hemangioblastoma
- Hemangioendothelioma
- Hemangioma thrombocytopenia syndrome
- Hemangiopericytoma
- Hemi 3 syndrome
- Hepatoblastoma
- Hereditary diffuse gastric cancer
- Hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell cancer
- Hereditary melanoma
- Hereditary multiple osteochondromas
- Hereditary paraganglioma-pheochromocytoma
- Hereditary renal cell carcinoma
- Hidradenocarcinoma
- Hodgkin lymphoma
- Hurthle cell thyroid cancer
- Hyaline fibromatosis syndrome
- Hyperparathyroidism-jaw tumor syndrome
- Hypopharyngeal cancer
- Indolent B cell lymphoma
- Infantile myofibromatosis
- Inflammatory breast cancer
- Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus
- Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor
- Insulinoma
- Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
- Intraneural perineurioma
- Intraocular melanoma
- Juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia
- Juvenile polyposis syndrome
- Kaposi sarcoma
- Kaposiform Hemangioendothelioma
- Klatskin tumor
- Krukenberg carcinoma
- Langerhans cell sarcoma
- Laryngeal cancer
- Ledderhose disease
- Leiomyosarcoma
- Lentigo maligna melanoma
- LEOPARD syndrome
- Leukemia subleukemic
- Leukemia, T-cell, chronic
- Lhermitte-Duclos disease
- Li-Fraumeni syndrome
- Linear nevus sebaceous syndrome
- Lip and oral cavity cancer
- Lipoblastoma
- Liposarcoma
- Lung adenocarcinoma
- Lymph Node Neoplasm
- Lymphoblastic lymphoma
- Lymphoma AIDS related
- Lymphoma, large-cell, immunoblastic
- Lymphomatoid papulosis
- Lymphosarcoma
- Maffucci syndrome
- Mahvash disease
- Malignant cylindroma
- Malignant eccrine spiradenoma
- Malignant germ cell tumor
- Malignant melanoma, childhood
- Malignant mesenchymoma
- Malignant mesothelioma
- Malignant mixed Mullerian tumor
- Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor
- Malignant Teratocarcinosarcoma
- Mantle cell lymphoma
- McCune-Albright syndrome
- Mediastinal endodermal sinus tumors
- Medulloblastoma
- Medulloblastoma, childhood
- Megalencephaly-capillary malformation syndrome
- Melanocytic lesions of CNS
- Melanoma astrocytoma syndrome
- Meningioma
- Merkel cell carcinoma
- Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast
- Metastatic insulinoma
- Metastatic squamous neck cancer with occult primary
- Microcystic adnexal carcinoma
- Microcystic lymphatic malformation
- Mosaic variegated aneuploidy syndrome
- Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
- Muir-Torre syndrome
- Multicentric Castleman Disease
- Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1
- Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2A
- Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2B
- Multiple fibrofolliculoma familial
- Multiple myeloma
- Multiple self healing squamous epithelioma
- Mycosis fungoides
- Myelocytic leukemia-like syndrome, familial, chronic
- Myelodysplastic syndromes
- Myeloid leukemia
- Myeloid sarcoma
- Myoepithelial carcinoma
- Myxoid liposarcoma
- N syndrome
- Nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Neural crest tumor
- Neuroblastoma
- Neurocutaneous melanosis
- Neuroendocrine carcinoma of the cervix
- Neuroepithelioma
- Neurofibromatosis type 2
- Neurofibromatosis-Noonan syndrome
- Neurofibrosarcoma
- Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome
- Nevus comedonicus syndrome
- Nevus of Ito
- Nijmegen breakage syndrome
- Nodular melanoma
- Non-functioning pancreatic endocrine tumor
- Non-involuting congenital hemangioma
- Non-seminomatous germ cell tumor
- Noonan syndrome
- Ocular melanoma
- Olfactory neuroblastoma
- Oligoastrocytoma
- Oligodendroglioma
- Ollier disease
- Onychocytic matricoma
- Optic pathway glioma
- Oral cancer
- Oral squamous cell carcinoma
- Orbital lymphangioma
- Orbital lymphoma
- Oropharyngeal cancer, adult
- Oslam syndrome
- Osteofibrous dysplasia
- Osteosarcoma
- Ovarian cancer
- Ovarian carcinosarcoma
- Ovarian epithelial cancer
- Ovarian germ cell tumor
- Ovarian low malignant potential tumor
- Ovarian small cell carcinoma
- Paget disease of the breast
- Painful orbital and systemic neurofibromas-marfanoid habitus syndrome
- Pancreatic adenoma
- Pancreatic cancer
- Pancreatoblastoma
- Papillary cystadenocarcinoma
- Papillary renal cell carcinoma
- Papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Paraganglioma and gastric stromal sarcoma
- Paranasal sinus cancer, adult
- Paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration
- Parathyroid carcinoma
- Pediatric T-cell leukemia
- Penile cancer
- Peripheral T-cell lymphoma
- Perlman syndrome
- Peutz-Jeghers syndrome
- PHACE syndrome
- Pheochromocytoma
- Philadelphia-negative chronic myeloid leukemia
- Phyllodes tumor of the breast
- Phyllodes tumor of the prostate
- Pilocytic astrocytoma
- Pilomatrixoma
- Pineal parenchymal tumors of intermediate differentiation
- Pineoblastoma
- Pituitary cancer
- Plasma cell leukemia
- Plasmablastic lymphoma
- Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma
- Pleuropulmonary blastoma
- Plexosarcoma
- POEMS syndrome
- Polycythemia vera
- Polyembryoma
- Polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma
- Primary central nervous system lymphoma
- Primary effusion lymphoma
- Primary liver cancer
- Primary malignant melanoma of the cervix
- Primary malignant melanoma of the conjunctiva
- Primary melanoma of the central nervous system
- Primary myelofibrosis
- Proliferating trichilemmal cyst
- Proteus syndrome
- Proteus-like syndrome
- Pseudomyxoma peritonei
- Radiation induced angiosarcoma of the breast
- Radiation induced cancer
- Radiation induced meningioma
- Rare adenocarcinoma of the breast
- Renal cell carcinoma 4
- Retinoblastoma
- Retroperitoneal liposarcoma
- Rhabdoid tumor
- Rhabdomyosarcoma alveolar
- Rhabdomyosarcoma embryonal
- Richter syndrome
- Ring dermoid of cornea
- Rombo syndrome
- Sacrococcygeal Teratoma
- Saethre-Chotzen syndrome
- Salivary gland cancer, adult
- Sarcoma botryoides
- Schinzel Giedion syndrome
- Schwannomatosis
- Secretory breast carcinoma
- Sertoli-leydig cell tumors
- Severe congenital neutropenia autosomal recessive 3
- Sezary syndrome
- Shwachman-Diamond syndrome
- Sideroblastic anemia pyridoxine-refractory autosomal recessive
- Simpson-Golabi-Behmel syndrome
- Sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma
- Sinus cancer
- Small cell carcinoma of the bladder
- Small cell lung cancer
- Small intestine cancer
- Soft tissue sarcoma
- Somatostatinoma
- Sotos syndrome
- Splenic neoplasm
- Stomach cancer
- Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma
- Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma
- Subependymoma
- Superficial spreading melanoma
- Supraglottic laryngeal cancer
- Supratentorial primitive neuroectodermal tumor
- Supraumbilical midabdominal raphe and facial cavernous hemangiomas
- Synovial sarcoma
- T-cell large granular lymphocyte leukemia
- T-cell lymphoma 1A
- T-cell/histiocyte rich large B cell lymphoma
- Teratoma with malignant transformation
- Testicular seminoma
- Testicular yolk sac tumor
- Thoracolaryngopelvic dysplasia
- Thymic epithelial tumor
- Thyroid cancer, follicular
- Thyroid cancer, medullary
- Tongue cancer
- Transient myeloproliferative syndrome
- Transitional cell cancer of the renal pelvis and ureter
- Transitional cell carcinoma
- Trichofolliculoma
- Trophoblastic tumor placental site
- Tuberous sclerosis complex
- Tufted angioma
- Turcot syndrome
- Tylosis with esophageal cancer
- Tyrosinemia type 1
- Undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma
- Unicentric Castleman disease
- Urachal adenocarcinoma
- Urachal cancer
- Urethral cancer
- Uterine Carcinosarcoma
- Uterine sarcoma
- Vaginal cancer
- Verrucous nevus acanthokeratolytic
- VIPoma
- Visual pathway and hypothalamic glioma, childhood
- Von Hippel-Lindau disease
- Vulvar cancer
- WAGR syndrome
- Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia
- Werner syndrome
- White sponge nevus of cannon
- Wilms tumor and radial bilateral aplasia
- Wilms’ tumor
- Wiskott Aldrich syndrome
- WT limb blood syndrome
- X-linked lymphoproliferative disease due to SH2D1A deficiency
- X-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome
- Xeroderma pigmentosum
- Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
- Zuska’s disease
Refereces
https://www.macmillan.org.uk/cancer-information-and-support/rare-cancers
https://rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/diseases-by-category/1/rare-cancers
